Please do not block ads on our site. Clicks on ads help us exist, grow and become more useful for you!
Calculation of heat losses in heating networks
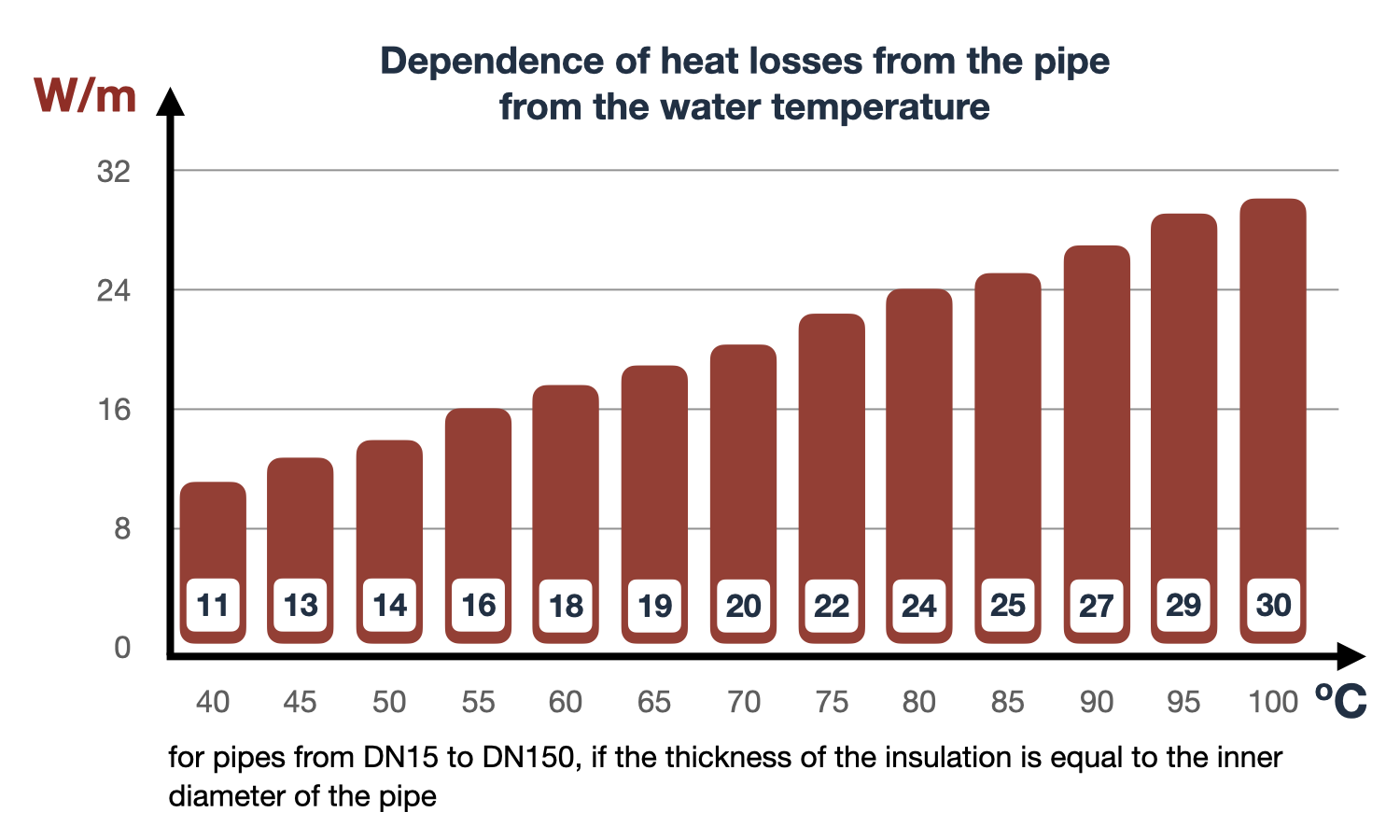
Interestingly, if the pipe is insulated with a layer equal to the inner diameter of the pipe, the heat loss from one meter of pipe for all diameters from DN15 to DN150 will be the same!
Calculation of heat losses in heat networks according to the Norms of thermal insulation of equipment and pipelines of heat networks.
The method of calculating heat losses is suitable for all pipelines covered by the Regulatory Methodology, except for systems with a subzero temperature of the working environment.
The amount of heat loss was calculated based on the normative density of the heat flow through the insulated surface of the pipeline. The methodology uses tabular data of specific heat losses from one meter of pipe, which are given in the Regulatory Methodology.
Estimated heat loss through pipelines of the heat network is determined by the formula:
Q = q · l · k · b
q – the specific normative value of heat loss from one meter of the pipe, W/m, at the average temperature of the hot-water and the given number of hours of operation per year;
k – the coefficient that takes into account additional heat losses from pipeline supports and shut-off valves;
b – the coefficient that takes into account the change in heat flow density through the thermal insulation layer made of polyurethane foam (PU foam) is determined by the Regulatory Methodology;
l – length of the pipeline section, m.
When calculating heat losses in heating networks, the annual average temperature of hot water should be taken.
Calculated temperatures in two-pipe water heating networks with quality regulation depending on Temperature curve of the heating system:
| Temperature curve of the heating system | Calculated temperatures по Regulatory Methodology Thermal insulation |
|---|---|
| 180-70 | supply 110°C return 50°C |
| 150-70 | supply 90°C return 50°C |
| 130-70 | supply 65°C return 50°C |
| 95-70 | supply 65°C return 50°C |
| 80-50 | supply 50°C return 45°C |
In heat networks with quantitative regulation, when calculating heat losses, the maximum temperature in the supply pipeline is used, and in the return 50°C.
This calculation does not reflect the actual heat loss through the pipelines, but only determines the normative value, which should not be exceeded, if the thickness of the thermal insulation was selected in accordance with the specified Regulatory Methodology.
 Online Calculations
Online Calculations


 EXAMPLE
EXAMPLE
